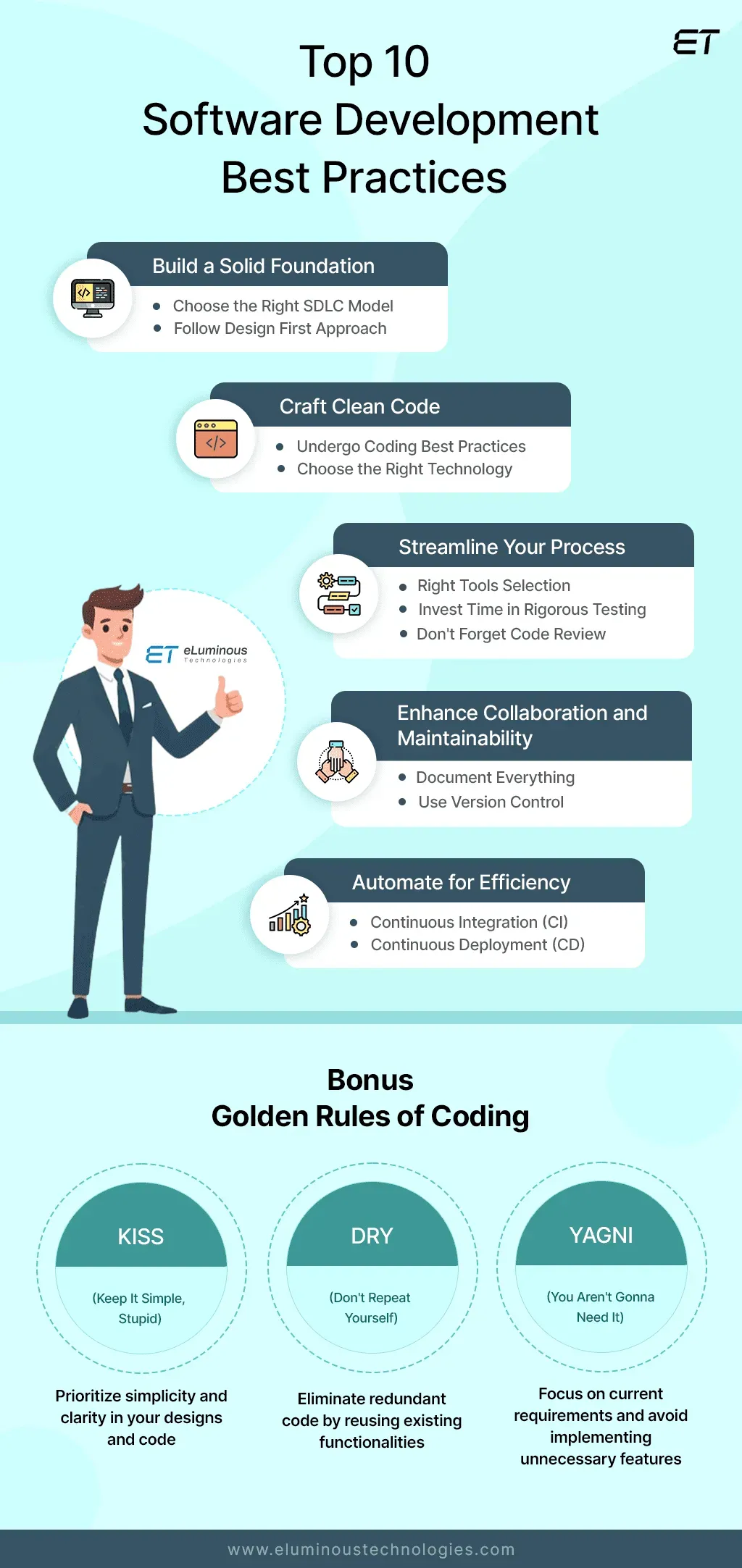
Software development best practices guide teams toward balancing speed with quality as they ship updates daily. By emphasizing repeatable processes, robust automation, and proactive risk management, organizations can achieve faster releases and safer releases without sacrificing quality. Implementing CI/CD best practices, test automation, and software deployment automation helps teams accelerate delivery while maintaining quality gates. Observability and measurable release metrics provide visibility into progress and help catch issues early. Taken together, these practices create a sustainable pattern of reliable releases that stakeholders can trust.
Put differently, the practice of dependable software delivery rests on repeatable workflows, automated checks, and risk-aware governance. Think of it as delivery engineering, quality assurance discipline, and release management that enables fast, safe updates. Related concepts like continuous integration pipelines, automated testing strategies, and deployment automation echo the same goals and help readers relate the ideas to practical workflows. Adopting this broader vocabulary helps teams align across development, operations, and security while improving search relevance.
Software development best practices for faster and safer releases
In an era where software teams ship updates daily, adopting Software development best practices helps create a predictable rhythm that balance speed with quality. By establishing repeatable processes, robust automation, and proactive risk management, organizations can push for faster releases without compromising safety. Clear definitions of done, shared standards, and observable release metrics reduce variability and build confidence that each change behaves as expected in production.
Operationalizing these practices means investing in test automation, deployment automation, and a culture of blameless learning. Start from core features, scale coverage over time, and tie automation to meaningful outcomes like faster releases and safer releases. Emphasize people and tooling: implement automated checks, maintain visibility into test results, and ensure your CI/CD workflows are designed to detect defects early and surface risks before customers are affected.
CI/CD best practices for safer releases and automated delivery
Continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) sits at the heart of modern software delivery. A robust CI/CD pipeline that runs unit tests, integration tests, and security checks on every commit turns manual toil into repeatable, reliable progress toward faster releases. In the CD phase, automated deployments to staging and production—with appropriate approvals and feature flags—minimize risk and accelerate value delivery.
Key components of CI/CD for safer releases include reproducible builds, comprehensive test suites (unit, integration, and contract tests), static and dynamic analysis, automated release gates, and progressive delivery techniques like canary releases or blue-green deployments. Observability and telemetry post-release help verify behavior, detect regressions quickly, and support safer, faster iterations across the software delivery lifecycle.
Frequently Asked Questions
What CI/CD best practices should teams adopt to achieve faster releases while ensuring safer releases?
A robust CI/CD strategy starts with fast, reproducible builds and a comprehensive test suite that runs on every commit. Implement automated builds, unit tests, integration tests, and contract tests, along with static and dynamic code analysis to catch quality and security issues early. Gate changes with automated checks, and use deployment techniques like canary releases or blue-green deployments, complemented by feature flags to minimize risk. Ensure environment parity across stages and have automated rollback plans for quick recovery. Measure success with observability metrics (cycle time, lead time, deployment frequency, change failure rate, MTTR) to drive continuous improvement.
How do test automation and software deployment automation contribute to faster releases and safer releases?
Test automation provides rapid, reliable feedback and scalable coverage—from unit tests to end-to-end scenarios—reducing manual toil and early defect detection. Deployment automation ensures repeatable, idempotent deployments and consistent environments, enabling frequent releases with lower risk and easy rollback if issues arise. Combine with feature flags and progressive delivery (canary, blue-green) to validate changes with minimal customer impact. Maintain visibility through observability and secure coding practices so velocity does not come at the expense of safety.
| Aspect | What it means | Key Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Core principles | Shared understanding of what to build, how to build, and how to verify it before it reaches customers. | Definition of done; automated checks; observable release metrics; emphasis on code quality and repeatable processes. |
| Balancing speed with safety | Faster releases rely on automation, standardized handoffs, and continuous verification of quality; speed without safety leads to instability. | Feedback loop from code commit to customer value; rigorous security, performance, and resilience checks. |
| The role of CI/CD in faster releases and safer releases | CI/CD automates building, testing, and releasing software; enables faster, repeatable processes. | Robust CI with unit/integration/security checks on every commit; automated deployment to staging/production with approvals and feature flags. |
| Quality assurance, testing, and test automation | Quality is built into the lifecycle; test automation reduces errors and speeds feedback. | Unit, integration, API/contract, end-to-end, performance/reliability tests; reliable, maintainable tests and good visibility. |
| Deployment automation and release management | Automating deployments reduces manual errors and enables frequent, reliable releases. | Idempotent steps; environment parity; feature flags and canaries; automated rollbacks; versioned configs and immutable infrastructure. |
| Security, compliance, and risk management | Security must be woven into development; automated checks reduce risk. | SAST/DAST in CI; dependency vulnerability checks; secrets management; automated policy enforcement; incident response/runbooks. |
| People, process, and tooling | Culture and collaboration are essential alongside technology. | Clear ownership; lightweight change management; current documentation; modern toolchain; ongoing training. |
| Measuring success and continuous improvement | Track metrics to guide improvements and sustain practices. | Cycle and lead time, deployment frequency, change failure rate, MTTR; blameless post-incident reviews; continuous improvement. |
| Practical steps to implement | A pragmatic, phased approach helps teams adopt practices gradually. | Map delivery pipeline; minimal viable CI/CD; automated quality gates; feature flags; align goals; foster blameless learning with retrospectives. |
Summary
Software development best practices provide a holistic framework for delivering software quickly and safely. By embracing robust CI/CD, comprehensive testing, deployment automation, security, and a culture of collaboration, teams can achieve faster releases without compromising reliability. The result is a scalable software delivery process that satisfies customers, reduces production incidents, and enables teams to innovate with confidence.