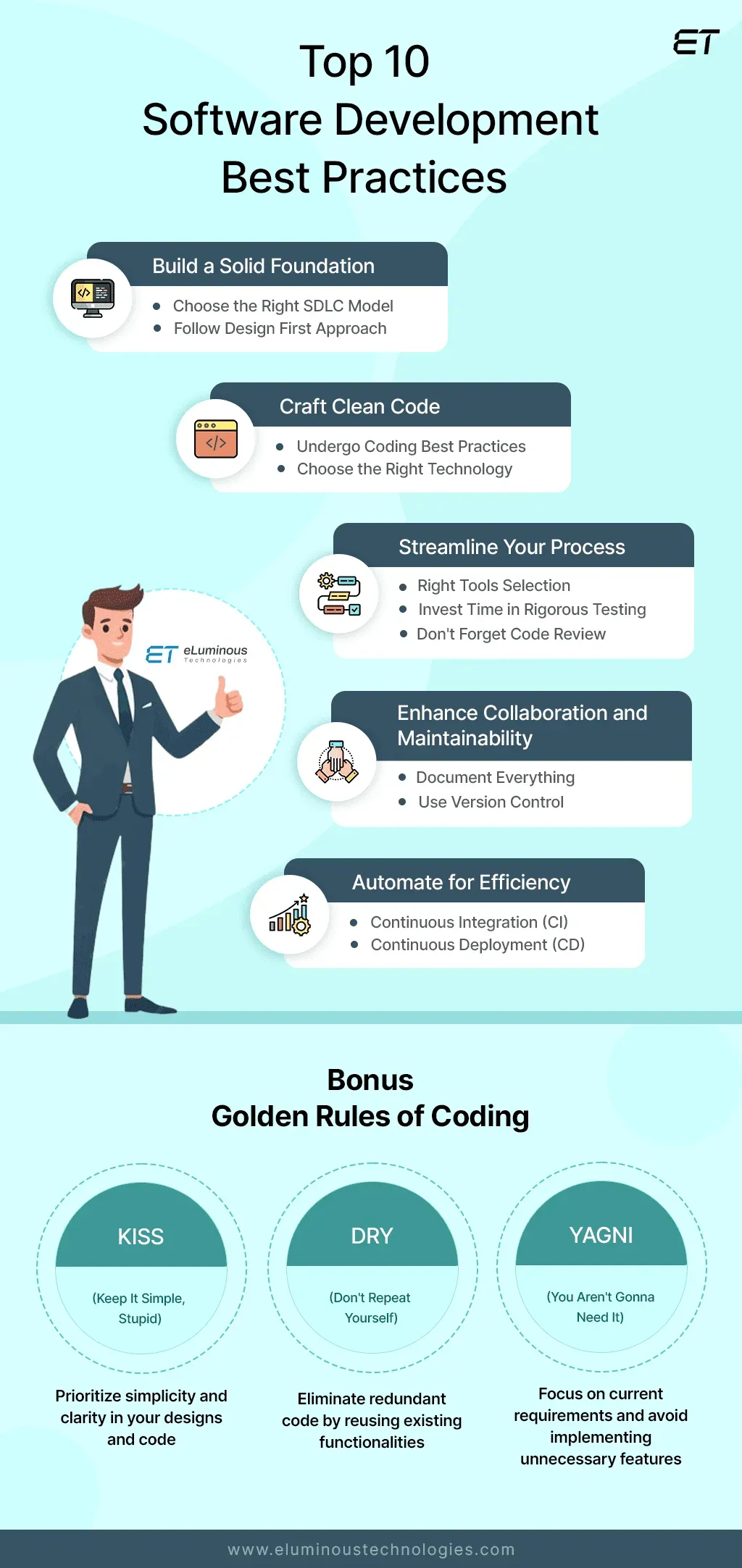
Software development best practices are a disciplined set of approaches that help teams deliver more quickly with fewer defects. In an industry where release cycles shrink from months to days, adopting repeatable, scalable methods ensures both quality and speed. Key practices span planning, design, testing, automation, and release management, and they align effort with measurable outcomes. For teams aiming to improve efficiency, integrating agile development best practices with robust testing and CI/CD pipelines is essential. By emphasizing code quality and bug prevention, teams build a foundation for reliable software through techniques like test-driven development benefits and release automation and CI/CD.
Viewed through the lens of software engineering maturity, these practices form a cohesive workflow rather than a collection of isolated tips. In this frame, teams discuss engineering excellence, disciplined development workflows, and quality-driven delivery, mapping to broader software engineering standards. Rather than focusing solely on coding, organizations emphasize end-to-end pipelines, automated checks, and rapid feedback loops that keep releases predictable. Concepts such as continuous integration and deployment and code quality and bug prevention underpin the lifecycle from commit to production. Test-driven development benefits are realized when tests guide design, ensuring maintainable code and fewer regressions. In practice, this translates to DevOps-aligned practices, release automation and CI/CD, and a culture of blameless postmortems to learn from failures. By framing the topic with alternative terms and related concepts, the article becomes more discoverable to readers searching for linked ideas. The goal remains to balance speed with reliability by implementing scalable patterns, repeatable processes, and measurable improvements.
Software development best practices: Accelerating delivery with quality and reliability
Software development best practices are the engine that powers fast, high-quality releases. In a market where release cycles shrink from months to days, teams must pair coding discipline with repeatable, scalable processes—clear goals, lightweight architecture guidelines, and automated checks that keep momentum without compromising safety. By integrating agile development best practices into planning and design, organizations align technology choices with business outcomes and set the stage for reliable delivery.
Investing in testing, continuous integration and deployment, and code quality and bug prevention yields faster feedback and lower risk. Test-driven development benefits become tangible as tests guide design and prevent regressions, while CI/CD pipelines automate builds, tests, and deployments to shrink lead time. Release automation and CI/CD reduce manual steps, enable canaries and feature flags, and improve release predictability.
From Agile to CI/CD: A practical roadmap for robust software delivery
A practical roadmap for robust software delivery starts with disciplined planning, scalable architecture, and a culture of collaboration. Start by embracing agile development best practices, keep backlogs groomed, and define acceptance criteria that translate into testable outcomes. Then implement a minimum viable CI/CD workflow that automatically builds, tests, and packages changes, so risk is caught early and feedback is rapid.
Expand the pipeline with automated testing layers—unit, integration, and end-to-end tests—paired with release automation to promote safe, frequent releases. Emphasize code quality and bug prevention as you grow, using static analysis, linting, and quality gates to keep the codebase healthy. Finally, monitor the system after release with observability dashboards to detect drift and accelerate incident response, closing the loop back to planning and improvement.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the core software development best practices that help teams deliver faster with fewer defects, leveraging agile development best practices, continuous integration and deployment, test-driven development benefits, code quality and bug prevention, and release automation and CI/CD?
Core software development best practices align people, processes, and technology to speed delivery while reducing defects. Key elements include planning and scalable architecture, agile development practices with short sprints and a well-groomed backlog, and a focus on code quality and bug prevention through linting, code reviews, and small, well-scoped functions. Testing strategies cover unit, integration, and end-to-end tests, anchored by the test-driven development benefits of designing code from tests. A robust CI/CD approach provides automatic builds, layered tests, and automated packaging, while release automation and CI/CD ensure repeatable, reliable deployments with feature flags and canary releases that minimize risk.
How can teams implement a practical 90-day plan to adopt software development best practices with CI/CD and testing while staying aligned with agile principles?
Adopt a staged plan that builds discipline gradually while delivering visible gains. First 30 days: audit current processes, establish a baseline, identify two bottlenecks, and define the Definition of Done; set up lightweight continuous integration checks. Days 31–60: implement one CI/CD improvement and start a focused testing initiative (emphasize unit and integration tests), refine the backlog, and tighten acceptance criteria. Days 61–90: expand automation to release processes, introduce release automation and canary or blue–green deployments, implement feature flags, and establish monitoring dashboards; conduct regular retrospectives to drive continuous improvement. This approach leverages agile development best practices and yields measurable improvements in code quality and deployment speed.
| Aspect | Core Principle / Focus | Key Benefits / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Planning, scope, and architecture that scale | Plan before coding; create lightweight architectural guides; define modular boundaries and extensible interfaces | Supports agility and easier adaptation to changing requirements; establishes guardrails for long-term scalability. |
| Agile development practices that keep teams aligned | Foster collaboration, incremental value, and fast feedback; maintain visible backlogs and short sprints | Keeps teams focused on customer outcomes; enables rapid experimentation and continuous learning. |
| Code quality and maintainability as a habit | Emphasize reading, testing, and extendable code via pair programming, thoughtful code reviews, and coding standards | Reduces defects, improves readability, and makes future changes easier and safer. |
| Testing strategies that catch defects early | Unit, integration, and end-to-end tests; use Test-Driven Development (TDD) where appropriate | Shortens feedback loops, increases confidence, and protects the codebase as it evolves. |
| Continuous integration, delivery, and release automation | Automated builds, layered test suites, packaging, and deployment; feature flags and canaries | Speeds up releases with lower risk and consistent quality; reduces manual steps and drift. |
| Release management, risk reduction, and observability | Semantic versioning, robust rollback plans, and comprehensive monitoring; canary/blue-green deployments | Minimizes impact of failures, shortens recovery time, and provides visibility into system health. |
| Collaboration, documentation, and knowledge sharing | Clear documentation, paired work, code reviews, and blameless postmortems | Reduces tribal knowledge, improves onboarding, and spreads best practices across the team. |
| Measurement and continuous improvement | Track metrics like cycle time, deployment frequency, MTTR, test coverage, and defect density | Drives data-informed improvements and sustains a culture of learning and refinement. |
Summary
Software development best practices