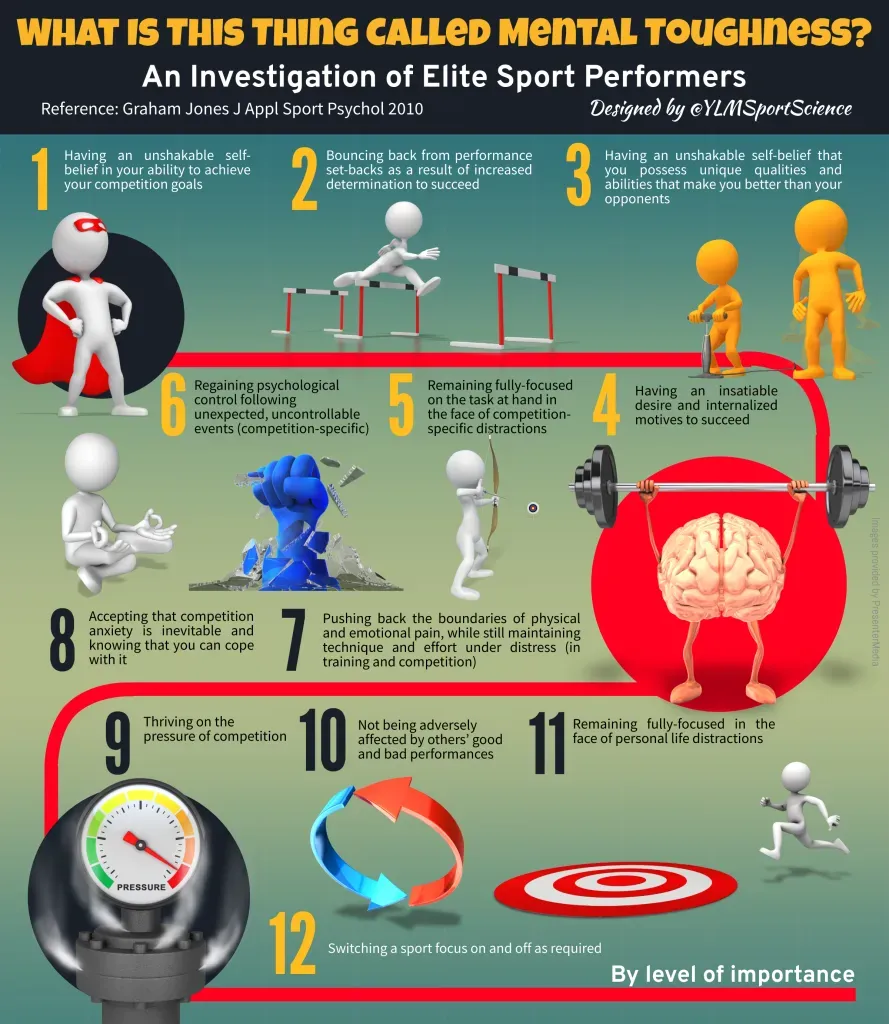
Mental toughness in sports is more than a buzzword; it’s a structured blend of behaviors, mindsets, and routines that help athletes perform under pressure. It explains why some athletes stay composed, rebound quickly from mistakes, and stay committed to long-term goals. In the high-stakes world of competition, focus and resilience are foundational skills that separate peak performers from the rest. This article connects the ideas to Sports psychology and practical strategies you can apply on and off the field. From pre-performance routines to adversity in sports, these elements build a durable competitive edge.
In other terms, this quality can be described as psychological resilience and cognitive endurance that athletes cultivate through deliberate practice. Sport psychologists study how mental fortitude emerges from routines, feedback loops, and the ongoing calibration of thoughts during competition. Another way to frame it is emotional regulation under pressure, where focus, confidence, and control over arousal drive better decisions. Programs labeled as mental toughness training or resilience coaching translate these ideas into accessible drills, routines, and performance simulations. Together, these LSI-aligned perspectives help readers connect daily practice with long-term competitive growth.
Mental toughness in sports: A sports psychology-driven path to focus and resilience
Mental toughness in sports is not just grit; it’s a structured integration of cognitive strategies, emotional regulation, and routine that helps athletes stay composed under pressure. Grounded in sports psychology, this approach translates scientific insights into practical tools—attention control, arousal management, and a growth mindset—that support focus and resilience in sports. By reframing pressure as a signal to align skills with intent, athletes learn to maintain precision even when spectators, time, or stakes increase. The idea that mental toughness is a fixed trait is replaced by a dynamic skillset that can be trained through deliberate practice and consistent pre-performance routines.
Developing mental toughness in sports involves specific training elements that reinforce reliable performance. Visualization and mental rehearsal create neural pathways that mirror real practice, while goal setting and self-monitoring translate intention into action. Growth mindset cultivation keeps motivation high after mistakes, and recovery practices—sleep, nutrition, and hydration—stabilize mood and cognitive function for the next challenge. Together, these components form a structured mental toughness training program that strengthens confidence under pressure and sustains long-term performance.
Adversity in sports: Strengthening performance through mental toughness training and routines
Adversity in sports is inevitable, but how athletes respond determines outcomes. Using a steady post-error reset, breath control, and a dependable pre-performance routine helps athletes stay focused when momentum shifts or when facing a high-stakes matchup. Stress inoculation training exposes athletes to controlled stressors in practice—such as time pressure or noisy environments—so the brain can regulate arousal more effectively during competition. In this way, focus and resilience in sports become reflexes rather than reactions to surprise.
Practical implementation combines individual work with team dynamics. Mental rehearsal, cue words, and micro-goals anchor attention during critical moments, while social support networks reinforce accountability and confidence. By aligning sports psychology insights with real-world scenarios—losing streaks, costly errors, or external distractions—athletes build a durable toolkit that translates preparation into performance. This holistic approach to adversity in sports emphasizes ongoing training, proper recovery, and adaptive strategies that sustain high performance across a demanding season.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is mental toughness in sports and how does sports psychology help athletes cultivate focus and resilience in sports?
Mental toughness in sports is the ability to stay composed, focused, and motivated when the stakes are high. In sports psychology, this is developed using evidence-based strategies to regulate arousal, control attention, and manage thoughts and self-talk, which strengthens focus and resilience in sports. Practical steps include creating a consistent pre-performance routine, using cue words, practicing breath control, and training under pressure so that performance becomes more automatic when it matters.
What mental toughness training strategies, including pre-performance routines, help athletes manage adversity in sports and perform under pressure?
Effective mental toughness training combines practical tools that translate to competition. Core strategies include mental rehearsal and visualization; clear goal setting and self-monitoring; fostering a growth mindset; prioritizing recovery, sleep, and nutrition; stress inoculation to tolerate pressure; and leveraging social support and team dynamics. Implement these by simulating pressure in practice, pairing cue words with micro-goals, developing a fast post-error reset, and embedding pre-performance routines to anchor attention. This approach also helps athletes confront adversity in sports by reframing setbacks as learning opportunities and building resilience over time.
| Aspect | Key Points | Practical Takeaways |
|---|---|---|
| Definition and Purpose | Mental toughness in sports is a structured set of behaviors, mindsets, and routines that help athletes perform under pressure, rebound from mistakes, and stay committed to long-term goals. It’s linked to sports psychology and focuses on staying composed, motivated, and effective when stakes rise. | Foster composure, clarify goals, and adopt a growth mindset through consistent practice and reflection. |
| Core Components | Key components include confidence under pressure, emotional control, cognitive flexibility, and consistent effort toward goals. Mental toughness is trainable, not fixed. | Develop these through deliberate practice and routines; monitor how thoughts influence actions. |
| Focus and Attention Strategies | Techniques to maintain sharp focus: pre-performance routines, attention control training, breath management, cue words and micro-goals, and post-error reset protocols. | Incorporate routines, practice breath pacing (e.g., six breaths per minute), use cue words, and establish a rapid post-error reset. |
| Training Approaches | Mental rehearsal/visualization, goal setting and self-monitoring, growth mindset cultivation, recovery, sleep and nutrition, stress inoculation training, and social support within teams. | Create a structured, long-term program; combine cognitive and physical recovery strategies; leverage social support to sustain motivation. |
| Real-World Applications | Apply concepts in scenarios such as losing streaks, high-pressure matchups, costly errors, distractions, and long seasons. | Use routines, arousal management, targeted micro-goals, and fast resets to maintain performance across conditions. |
| Common Pitfalls | Overreliance on positive thinking without actionable steps, neglecting sleep/recovery, and treating mental toughness as a one-size-fits-all solution. | Personalize strategies to sport, position, personality, and level of competition; ensure recovery and individualized plans. |
Summary
This table summarizes the key points about mental toughness in sports, including its purpose, core components, focus strategies, training approaches, real-world applications, and common pitfalls.