Cloud, Edge, and Beyond sets the vision for how modern technology architecture must evolve to meet speed, scalability, and resilience. As organizations migrate workloads to the cloud and push intelligence toward the network edge, architectures become interwoven across data centers, regional hubs, and increasingly capable devices at the edge. Smart design choices rely on clear governance, observable performance, and a focus on cloud architecture to align capabilities with goals. The approach supports real-time analytics, resilient services, and secure data movement, while offering developers a coherent blueprint for building distributed applications across environments. This introduction equips architects, operators, and product leaders with practical decisions that balance speed, cost, risk, and innovation.
Viewed through an LSI-inspired lens, the topic can be framed as cloud-first infrastructure, edge processing, and distributed platforms that coordinate across on-premises and public clouds. Alternative terms such as hybrid cloud environments, microservices orchestration, and data pipelines convey the same core ideas while enriching the search context. Architects also consider data gravity, service meshes, and observability to ensure security and performance across sites. In practice, teams map workloads to optimal locations, enabling low latency, resilience, and governance across multi-cloud and edge-enabled ecosystems.
Cloud, Edge, and Beyond: Designing a Unified Modern Technology Architecture
Cloud, Edge, and Beyond represents a pragmatic blueprint for orchestrating resources across centralized cloud platforms, edge sites, and emerging computing paradigms. By aligning cloud architecture patterns with edge computing capabilities, organizations can achieve the right balance of scalability, resilience, and proximity to data sources. This approach leverages a hybrid cloud mindset and distributed systems principles to minimize latency while preserving governance and security across environments.
With this framework, architects map workloads to the most appropriate layer, design patterns for data orchestration, and implement observability across sites. Key considerations include data residency, service discovery, and automated policy enforcement as part of modern technology architecture. The cloud-edge continuum enables real-time analytics, AI at the edge, and robust disaster recovery through cross-environment collaboration.
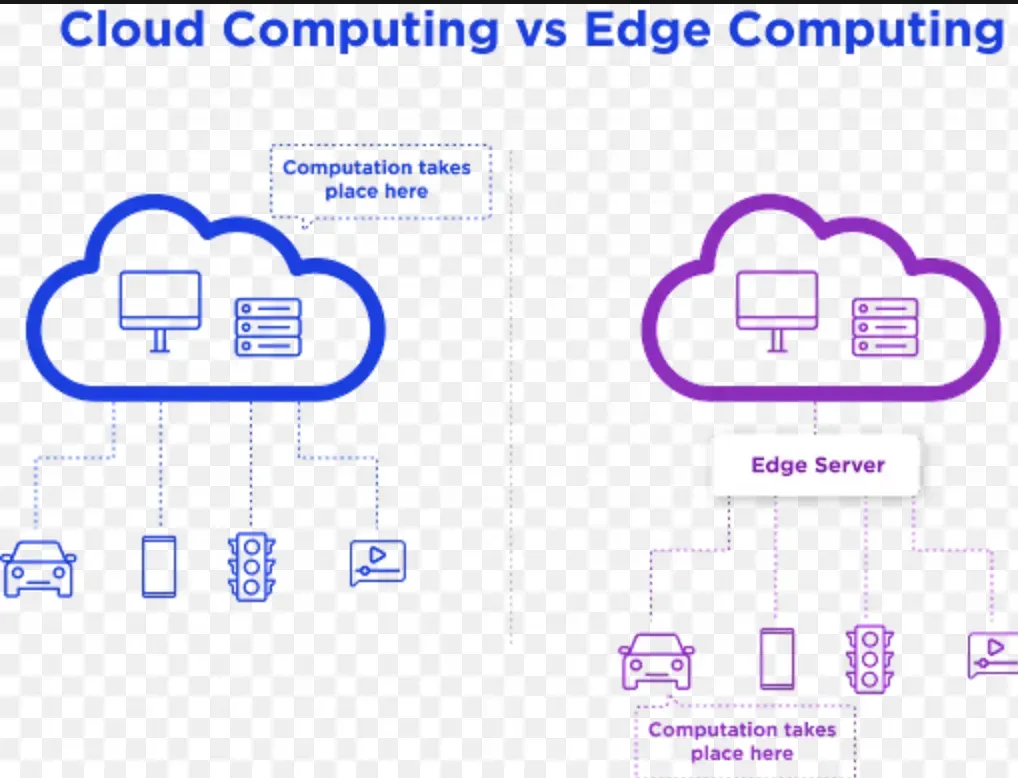
Practical Patterns for Cloud, Edge, and Beyond: From Multi-Cloud to Edge-to-Cloud Orchestration
Implementing a multi-cloud and edge-to-cloud orchestration strategy requires careful attention to data gravity, service mesh, and data pipelines. By applying distributed systems concepts, organizations can achieve consistent governance, resilient messaging, and scalable microservices across sites. This aligns with cloud architecture principles while embracing edge computing realities such as intermittent connectivity and hardware heterogeneity.
Adopting an observability-first approach and data-centric design helps teams monitor performance, security, and compliance across hybrid cloud deployments. Event-driven architectures, data streaming, and automated validation support modern technology architecture that spans the cloud, edge, and beyond. In practice, this means designing for data locality, policy-as-code, and robust security across networks.
Frequently Asked Questions
In Cloud, Edge, and Beyond, how should organizations guide workload placement across cloud architecture and edge computing within a modern technology architecture?
Cloud, Edge, and Beyond guides workload placement by balancing latency, data gravity, governance, and cost. Use cloud architecture for scalable resources, central governance, and global reach; deploy edge computing for low latency, local data processing, and real-time decisions. Consider regulatory requirements and connectivity when choosing between cloud and edge, and use hybrid cloud patterns such as edge-to-cloud orchestration to coordinate workloads, maintain data synchronization, and enforce security and observability across environments.
What architectural patterns and practices are essential in Cloud, Edge, and Beyond to achieve resilience and observability across hybrid cloud and distributed systems?
Key patterns include a multi-cloud strategy, edge-to-cloud orchestration, event-driven microservices, and data-centric design that optimize where data is stored and processed. Apply service mesh, data pipelines, and observability across domains to unify logs, metrics, and traces. Emphasize zero-trust security, secure software supply chains, and policy-as-code for governance, ensuring resilience and compliance across cloud, edge, and beyond in a modern technology architecture.
| Theme | Key Points | Implications | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Architecture Foundations | Scale resources on demand; resilience via redundancy and graceful degradation; security, governance, observability, and data management across services. | Align app requirements with platform capabilities; adopt managed containers, serverless, database services, and global content delivery; implement governance and monitoring. | Auto-scaling, retry strategies, encryption, audit trails, logs/metrics/tracing. |
| The Edge: Bringing Compute to the Data’s doorstep | Move processing closer to data sources to reduce latency, save bandwidth, and enable real-time decisions. | Edge workloads must be lightweight, handle intermittent connectivity, and work across diverse hardware; synchronize with cloud when possible. | Containerized edge apps, local AI inference, eventual data consistency, secure boot, and edge-to-cloud integration. |
| Hybrid Cloud and Distributed Systems: The Beyond | Blend on-premises with multiple public clouds and apply distributed system principles across sites; consider data gravity and governance across domains. | Unified management plane; patterns like service mesh; data pipelines; observability across cloud and edge; consistent security controls. | Unified control planes, data pipelines, event-driven architectures, and data-placement strategies. |
| Architectural Patterns for Cloud, Edge, and Beyond | Adopt patterns to operationalize concepts: multi-cloud, edge-to-cloud orchestration, event-driven microservices, data-centric design, observability-first. | Telemetry-first design reduces mean time to recovery; resilience; cross-site observability; scalable, decoupled systems. | Multi-cloud workloads; edge-to-cloud orchestration; event-driven microservices; data-centric design. |
| Security and Compliance Across the Stack | IAM, encryption in transit and at rest, secure software supply chains, and continuous vulnerability management; zero-trust; privacy-by-design. | Enforce policy as code, automated audits, and consistent security controls across environments; continuous compliance checks. | IAM roles, TLS encryption, SBOMs, and automated security scans. |
| Practical Considerations for Teams | Start with a workload placement strategy; automate provisioning with infrastructure as code; emphasize observability; design for resilience; foster cross-team collaboration. | Governance that supports speed, consistent practices, and alignment across developers, platform, and security teams. | IaC pipelines, automated provisioning, centralized tracing, resilient retry logic, and cross-team collaboration practices. |
Summary
Cloud, Edge, and Beyond describes a holistic approach to modern technology architecture, blending scalable cloud capabilities with edge computing and beyond-cloud patterns to deliver low-latency, resilient, and governed systems. It emphasizes deliberate workload placement, robust governance, and a culture of continuous improvement. As you plan or refactor infrastructure, prioritize effective cloud design, strategic edge deployment, and thoughtful beyond-cloud patterns to build architectures that meet evolving business needs and delight customers, partners, and stakeholders.